Latest Guidance Updates16 April 2024: updated recommendation in the section on Referral for Women with Suspected or Confirmed Endometriosis. NICE also updated recommendations on treatment of endometriosis when fertility is a priority, which is not included in this summary. |
Overview
This Guidelines summary provides information for primary care on signs and symptoms, diagnosis and referral, and pharmacological pain management of endometriosis. For a complete set of recommendations, refer to the full guideline.
Reflecting on your Learnings
Reflection is important for continuous learning and development, and a critical part of the revalidation process for UK healthcare professionals. Click here to access the Guidelines Reflection Record.
Endometriosis Information and Support
- Be aware that endometriosis can be a long-term condition, and can have a significant physical, sexual, psychological and social impact. Women may have complex needs and require long-term support.
- Assess the individual information and support needs of women with suspected or confirmed endometriosis, taking into account their circumstances, symptoms, priorities, desire for fertility, aspects of daily living, work and study, cultural background, and their physical, psychosexual and emotional needs.
- Provide information and support for women with suspected or confirmed endometriosis, which should include:
- what endometriosis is
- endometriosis symptoms and signs
- how endometriosis is diagnosed
- treatment options
- local support groups, online forums and national charities, and how to access them.
- If women agree, involve their partner (and/or other family members or people important to them) and include them in discussions. For more guidance on providing information to people and involving family members and carers, see the NICE guideline on patient experience in adult NHS services.
Endometriosis Symptoms and Signs
- Suspect endometriosis in women (including young women aged 17 and under) presenting with 1 or more of the following symptoms or signs:
- chronic pelvic pain
- period-related pain (dysmenorrhoea) affecting daily activities and quality of life
- deep pain during or after sexual intercourse
- period-related or cyclical gastrointestinal symptoms, in particular, painful bowel movements period-related or cyclical urinary symptoms, in particular, blood in the urine or pain passing urine
- infertility in association with 1 or more of the above.
- Inform women with suspected or confirmed endometriosis that keeping a pain and symptom diary can aid discussions.
- Offer an abdominal and pelvic examination to women with suspected endometriosis to identify abdominal masses and pelvic signs, such as reduced organ mobility and enlargement, tender nodularity in the posterior vaginal fornix, and visible vaginal endometriotic lesions.
- If a pelvic examination is not appropriate, offer an abdominal examination to exclude abdominal masses.
Referral for Women With Suspected or Confirmed Endometriosis
- Consider referring women to a gynaecology service for an ultrasound or gynaecology opinion if:
- they have severe, persistent or recurrent symptoms of endometriosis
- they have pelvic signs of endometriosis or
- initial management is not effective, not tolerated or is contraindicated.
- Refer women to a specialist endometriosis service (endometriosis centre) if they have suspected or confirmed:
- deep endometriosis involving the bowel, bladder or ureter, or
- endometriosis outside the pelvic cavity.
- Consider referring young women (aged 17 and under) with suspected or confirmed endometriosis to a paediatric and adolescent gynaecology service, gynaecology service or specialist endometriosis service (endometriosis centre), depending on local service provision.
Diagnosing Endometriosis
- Do not exclude the possibility of endometriosis if the abdominal or pelvic examination, ultrasound or MRI are normal. If clinical suspicion remains or symptoms persist, consider referral for further assessment and investigation.
Ultrasound
- Consider transvaginal ultrasound:
- to investigate suspected endometriosis even if the pelvic and/or abdominal examination is normal
- to identify endometriomas and deep endometriosis involving the bowel, bladder or ureter.
- If a transvaginal scan is not appropriate, consider a transabdominal ultrasound scan of the pelvis.
Serum CA125
- Do not use serum CA125 to diagnose endometriosis.
- If a coincidentally reported serum CA125 level is available, be aware that:
- a raised serum CA125 (that is, 35 IU/ml or more) may be consistent with having endometriosis
- endometriosis may be present despite a normal serum CA125 (less than 35 IU/ml).
Staging Systems
- Offer endometriosis treatment according to the woman’s symptoms, preferences and priorities, rather than the stage of the endometriosis.
- When endometriosis is diagnosed, the gynaecologist should document a detailed description of the appearance and site of endometriosis.
Monitoring for Women With Confirmed Endometriosis
- Consider outpatient follow‑up (with or without examination and pelvic imaging) for women with confirmed endometriosis, particularly women who choose not to have surgery, if they have:
- deep endometriosis involving the bowel, bladder or ureter or
- 1 or more endometrioma that is larger than 3 cm.
Pharmacological Pain Management
Analgesics
- For women with endometriosis-related pain, discuss the benefits and risks of analgesics, taking into account any comorbidities and the woman’s preferences.
- Consider a short trial (for example, 3 months) of paracetamol or a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) alone or in combination for first-line management of endometriosis-related pain.
- If a trial of paracetamol or an NSAID (alone or in combination) does not provide adequate pain relief, consider other forms of pain management and referral for further assessment.
Neuromodulators and Neuropathic Pain Treatments
- For recommendations on using neuromodulators to treat neuropathic pain, see the NICE guideline on neuropathic pain.
Hormonal Treatments
- Explain to women with suspected or confirmed endometriosis that hormonal treatment for endometriosis can reduce pain and has no permanent negative effect on subsequent fertility.
- Offer hormonal treatment (for example, the combined oral contraceptive pill or a progestogen) to women with suspected, confirmed or recurrent endometriosis.
In September 2017, this was off-label use for some combined oral contraceptive pills or progestogens. See NICE's information on prescribing medicines.
- If initial hormonal treatment for endometriosis is not effective, not tolerated or is contraindicated, refer the woman to a gynaecology service, specialist endometriosis service (endometriosis centre) or paediatric and adolescent gynaecology service for investigation and treatment options.
Non-pharmacological Management
- Advise women that the available evidence does not support the use of traditional Chinese medicine or other Chinese herbal medicines or supplements for treating endometriosis.
Endometriosis Algorithm
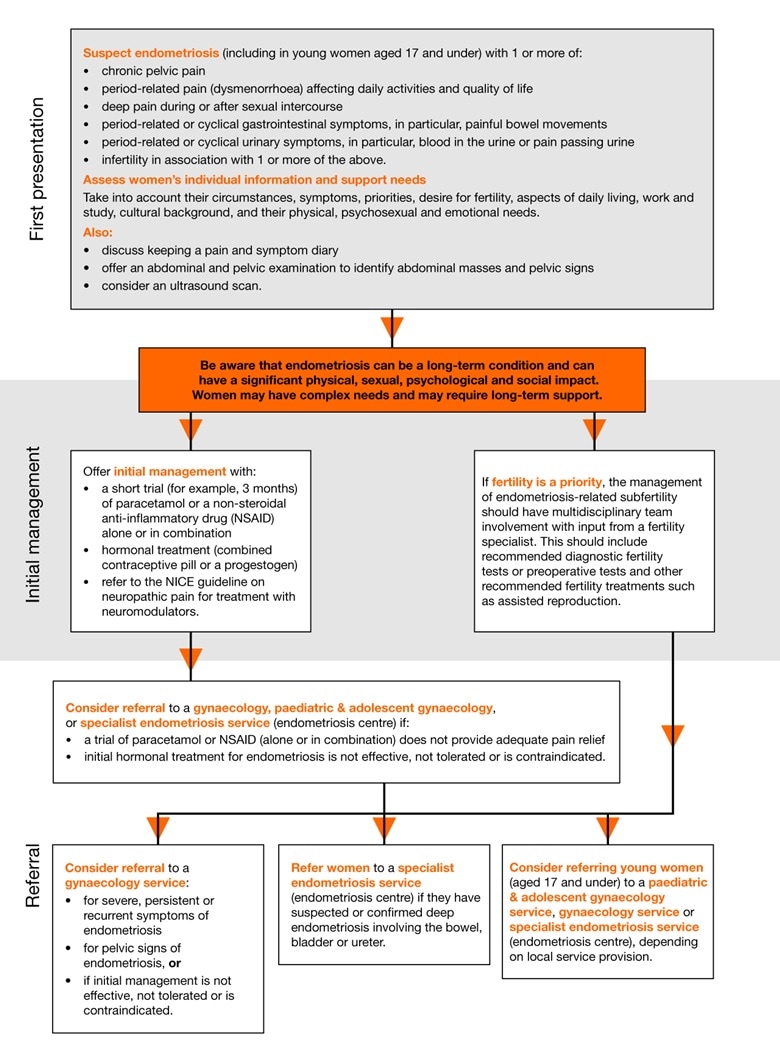
The full algorithm can be found at nice.org.uk/ng73.

